PostgreSQL NTILE Function
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PostgreSQL NTILE() function to divide ordered rows in the partition into a specified number of ranked buckets.
Introduction to PostgreSQL NTILE() function
The PostgreSQL NTILE() function allows you to divide ordered rows in the partition into a specified number of ranked groups as equal size as possible. These ranked groups are called buckets.
The NTILE() function assigns each group a bucket number starting from 1. For each row in a group, the NTILE() function assigns a bucket number representing the group to which the row belongs.
The syntax of the NTILE() function is as follows:
NTILE(buckets) OVER (
[PARTITION BY partition_expression, ... ]
[ORDER BY sort_expression [ASC | DESC], ...]
)Let’s examine the syntax in detail:
buckets
The buckets represents the number of ranked groups. It can be a number or an expression that evaluates to a positive integer value (greater than 0) for each partition. The buckets must not be nullable.
PARTITION BY
The PARTITION BY clause distributes rows into partitions to which the function is applied.
The PARTITION BY clause is optional. If you skip it, the function treats the whole result set as a single partition.
ORDER BY
The ORDER BY clause sorts rows in each partition to which the function is applied.
The ORDER BY clause is optional. However, you should always use the ORDER BY clause to get an expected result.
Note that if the number of rows is not divisible by the buckets, the NTILE() function returns groups of two sizes with the difference by one. The bigger groups always come before the smaller groups in the order specified by the ORDER BY clause.
PostgreSQL NTILE() function examples
Let’s take some examples of using the NTILE() function.
We’ll use the sales_stats table created in the CUME_DIST() function tutorial to demonstrate the NTILE() function.
SELECT
year,
name,
amount
FROM
actual_sales
ORDER BY
year, name;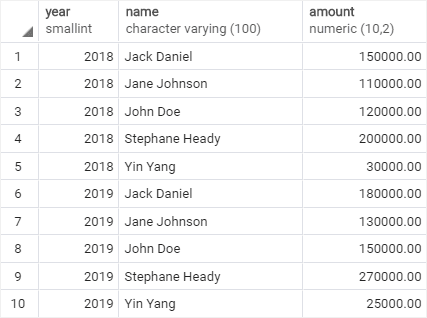
1) Using PostgreSQL NTILE() function over a result set example
This example uses the NTILE() function to distribute rows into 3 buckets:
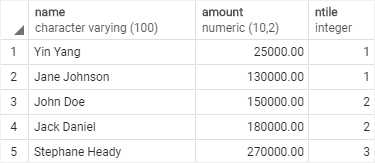
SELECT
name,
amount,
NTILE(3) OVER(
ORDER BY amount
)
FROM
sales_stats
WHERE
year = 2019;Here is the output:
2) Using PostgreSQL NTILE() function over a partition example
This example uses the NTILE() function to divide rows in the sales_stats table into two partitions and 3 buckets for each:
SELECT
name,
amount,
NTILE(3) OVER(
PARTITION BY year
ORDER BY amount
)
FROM
sales_stats;Here is the result set:
 In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the PostgreSQL
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the PostgreSQL NTILE() function to distribute ordered rows within a partition into a specified number of ranked groups.